Importance of ETL and ELT
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) are two common approaches for managing data pipelines. They matter today because AI and analytics systems depend on clean, well-structured data, and the order of operations, whether transformation happens before or after loading, can dramatically affect efficiency, cost, and flexibility. These methods are foundational to how organizations prepare data for decision-making and model training.
For social innovation and international development, ETL and ELT matter because mission-driven organizations often work with constrained resources and varied data sources. Choosing the right approach can determine whether a project is sustainable, scalable, and inclusive, or whether it struggles under technical and financial pressures.
Definition and Key Features
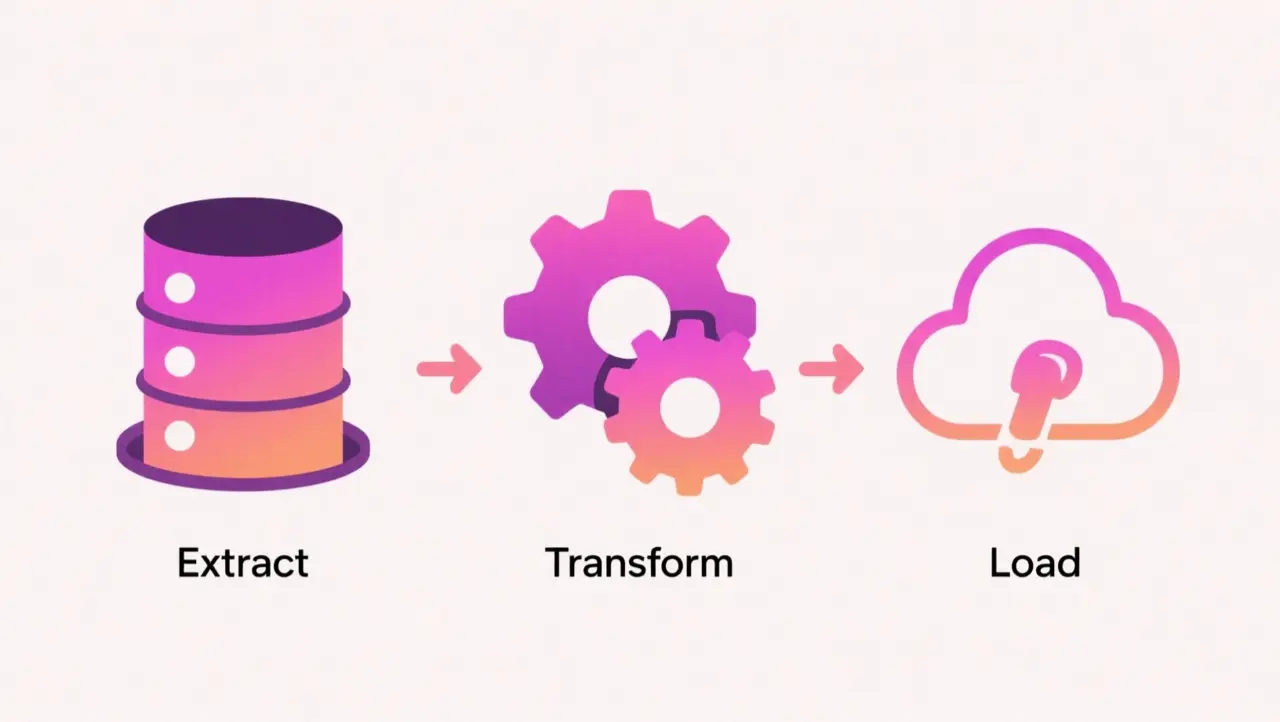
In ETL, data is extracted from sources, transformed into the desired format, and then loaded into a database or data warehouse. This method has been widely used in traditional analytics environments, where storage was limited and transformation upfront ensured consistency. ELT reverses the process: data is extracted, loaded in raw form into a warehouse or lake, and transformed afterward using the power of modern storage and processing systems.
They are not the same as simple data migration, which moves data without restructuring. Nor are they equivalent to machine learning pipelines, which sit further downstream. ETL and ELT are specific strategies for shaping data so it can be analyzed or used by AI in reliable and repeatable ways.
How this Works in Practice
In practice, ETL is useful when data requires heavy cleaning and consistent formatting before it can be stored. It ensures data quality but can be slower and less scalable. ELT takes advantage of cloud storage and compute, allowing organizations to load data quickly and then transform it as needed. This flexibility supports iterative analysis and experimentation, which are common in AI workflows.
The choice between ETL and ELT depends on context. ETL may be better for smaller organizations with structured data needs and limited computing resources. ELT may be better for those leveraging cloud infrastructure and handling diverse or rapidly growing datasets. Both approaches can be combined in hybrid systems where different data streams have different requirements.
Implications for Social Innovators
ETL and ELT directly shape how mission-driven organizations handle information. Health programs may use ETL to standardize patient records across clinics, ensuring consistency before analysis. Education platforms may prefer ELT to ingest raw student performance data and transform it dynamically for different learning models. Humanitarian agencies can benefit from ELT when combining diverse, fast-moving crisis datasets into centralized repositories for rapid response.
By choosing the right approach, organizations can align data workflows with their mission, ensuring that information is usable, timely, and sustainable for impact.