Importance of WebSockets
WebSockets are a communication protocol that provides full-duplex, persistent connections between clients and servers over a single TCP connection. Unlike traditional HTTP, which is request-response based, WebSockets allow both parties to send data at any time once the connection is established. Their importance today lies in enabling real-time communication for applications such as chat, live dashboards, collaborative tools, and AI-driven assistants.
For social innovation and international development, WebSockets matter because many mission-driven services rely on immediacy. From delivering timely health alerts to enabling interactive education tools, WebSockets support experiences that cannot depend on slow, one-way data exchanges.
Definition and Key Features
WebSockets begin as an HTTP handshake, after which the protocol upgrades to a persistent, bidirectional connection. This allows messages to flow continuously without the overhead of opening and closing new connections. The protocol is lightweight and efficient, making it well-suited for applications requiring instant updates and constant communication.
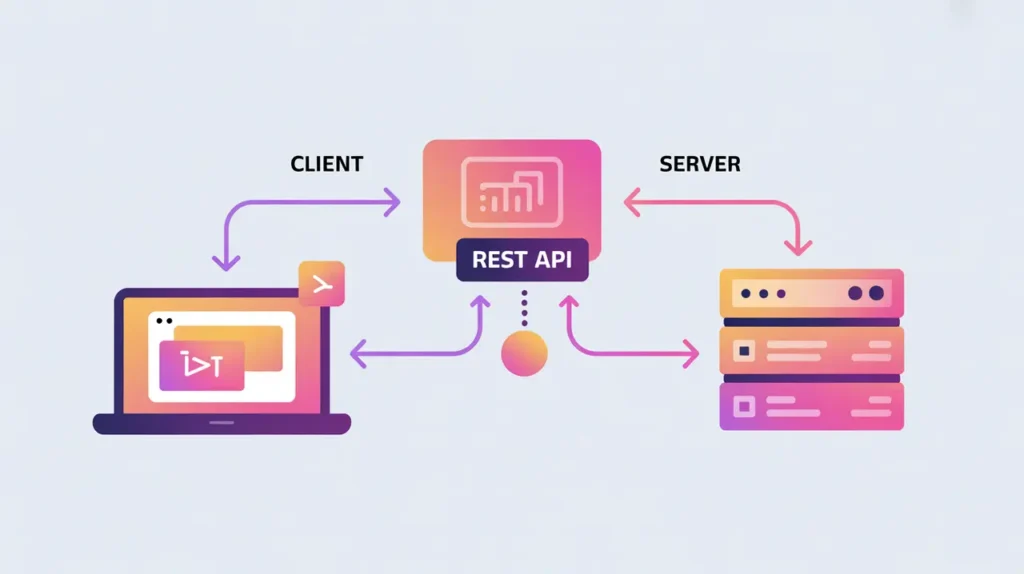
WebSockets are not the same as REST APIs, which rely on clients polling servers for updates. Nor are they equivalent to gRPC, which emphasizes structured, high-performance communication across microservices. WebSockets are designed for continuous, event-driven communication between clients and servers, with simplicity and responsiveness at their core.
How this Works in Practice
In practice, WebSockets are used in chat applications, collaborative editing tools, streaming dashboards, and AI assistants that provide live responses. They can be combined with protocols like STOMP or integrated into broader frameworks to manage messaging at scale. Servers and clients maintain open channels, reducing latency for updates and creating more interactive experiences.
Challenges include handling scalability as the number of persistent connections grows, ensuring security against hijacking or injection attacks, and managing reconnections in unstable network environments. Despite these challenges, WebSockets remain a powerful solution for enabling real-time interactivity.
Implications for Social Innovators
WebSockets empower mission-driven organizations to build responsive and engaging digital tools. Health platforms can deliver real-time telemedicine consultations or live monitoring of patient data. Education systems can support collaborative online classrooms where students and teachers interact instantly. Humanitarian agencies can use WebSockets for live crisis dashboards that update continuously as new information arrives.
By enabling persistent, real-time connections, WebSockets give organizations the ability to deliver timely, interactive services that build trust and engagement across communities.