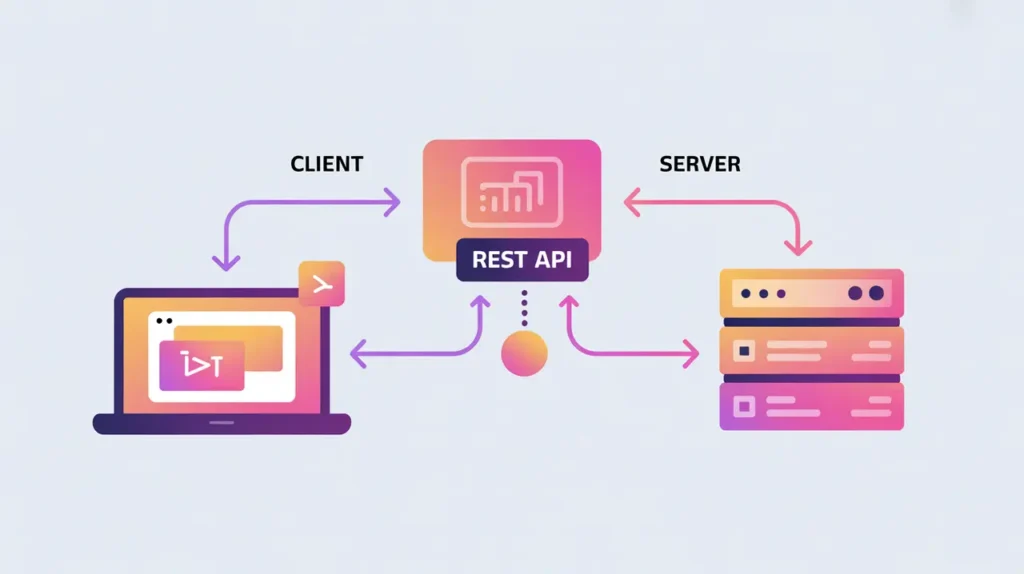
Importance of GraphQL
GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs that allows clients to request exactly the data they need, no more and no less. Developed by Facebook in 2012 and open-sourced in 2015, it was designed to overcome limitations of REST by reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data. Its importance today lies in the efficiency and flexibility it brings to modern applications, especially those with complex, data-rich interfaces.
For social innovation and international development, GraphQL matters because mission-driven organizations often work with limited bandwidth and fragmented data systems. By delivering lean, customized responses, GraphQL helps conserve resources while still providing the detail needed for health, education, and humanitarian decision-making.
Definition and Key Features
GraphQL defines a strong schema that describes the data available, and clients specify their exact requirements in a single query. The server responds with data that mirrors the structure of the request. This approach avoids multiple round-trips to different endpoints, streamlining interactions and improving efficiency for both clients and servers.
GraphQL is not the same as REST, which relies on multiple endpoints and fixed data structures. Nor is it equivalent to database query languages like SQL, as GraphQL queries are executed against an API layer that fetches from one or more underlying data sources. GraphQL focuses on flexibility in how data is retrieved and delivered to clients.
How this Works in Practice
In practice, GraphQL enables developers to combine data from multiple services into a single query, making it particularly useful for applications that display complex dashboards or interact with diverse systems. It supports features like introspection (allowing clients to explore the schema) and strong typing, which improves reliability. GraphQL APIs can also evolve without breaking clients, since new fields can be added while old ones remain accessible.
Challenges include the risk of overly complex queries that strain servers, the need for caching strategies that differ from REST, and the learning curve for organizations unfamiliar with schema design. Security is also critical, as GraphQL endpoints must guard against query abuse and ensure sensitive data is not unintentionally exposed.
Implications for Social Innovators
GraphQL provides mission-driven organizations with efficiency and adaptability in data access. Health platforms can aggregate patient data, diagnostics, and treatment histories from multiple systems into one query. Education platforms can deliver customized content and assessment data tailored to each student’s needs. Humanitarian agencies can unify crisis data from surveys, satellites, and partner reports into a single, coherent response for decision-making.
By enabling precise, flexible, and resource-conscious data retrieval, GraphQL helps organizations build smarter systems that operate effectively in diverse and bandwidth-constrained environments.