Importance of Balanced Scorecard
Balanced scorecard provides organizations with a structured way to track performance beyond financial measures. It helps align strategy with day-to-day operations by incorporating perspectives such as customer value, internal processes, and learning and growth. For nonprofits, governments, and social enterprises, the balanced scorecard matters because it ensures accountability while keeping mission, impact, and sustainability in focus.
Definition and Features
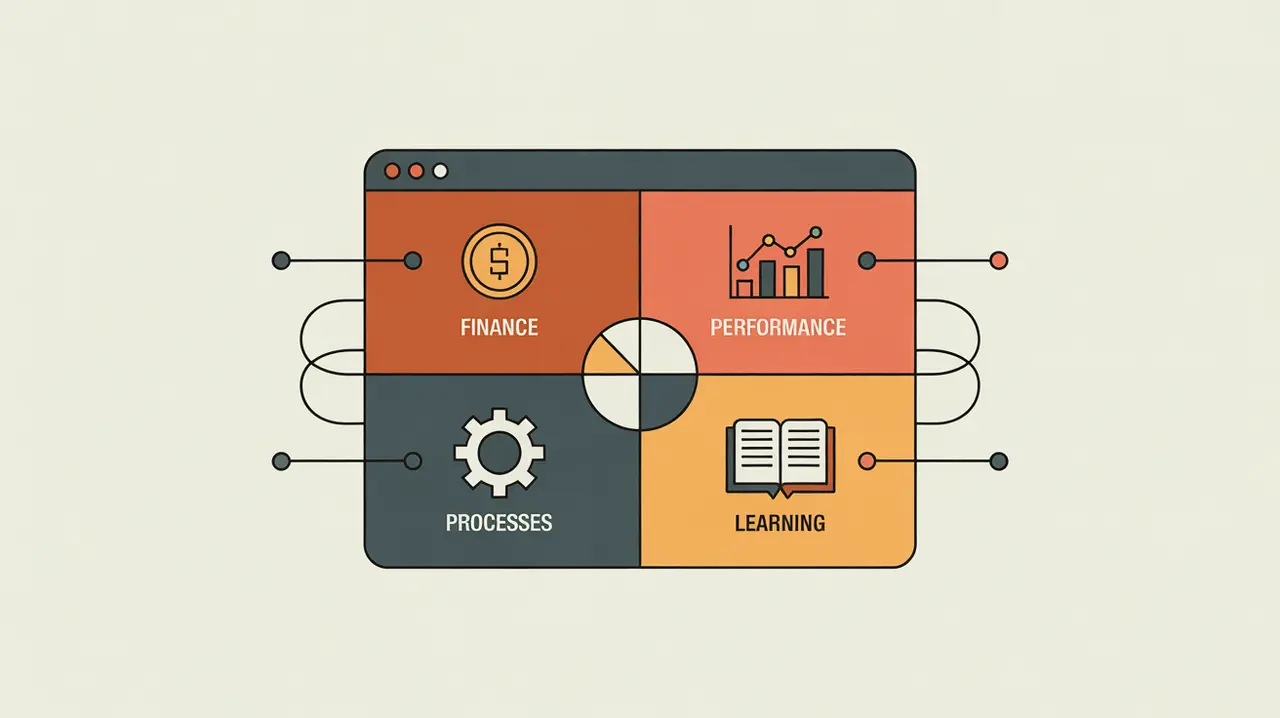
Balanced scorecard is a strategic performance management framework that evaluates organizational health across multiple dimensions. Its defining features include:
- Financial Perspective – tracks financial stability and resource efficiency.
- Customer/Beneficiary Perspective – measures satisfaction, outcomes, and service quality.
- Internal Process Perspective – monitors efficiency and effectiveness of operations.
- Learning and Growth Perspective – focuses on staff development, innovation, and organizational capacity.
- Alignment – links long-term strategy with short-term actions.
How this Works in Practice
In practice, nonprofits may adapt the balanced scorecard to include mission-related goals alongside financial and operational indicators. For example, a health NGO might track fundraising efficiency, patient satisfaction, service delivery times, and staff training rates. Governments have also used the framework to modernize public administration and improve service delivery. Challenges include selecting meaningful indicators, avoiding excessive measurement, and ensuring data is used for learning rather than just compliance.
Implications for Social Innovation
Balanced scorecard supports social innovation by promoting holistic performance tracking that integrates mission outcomes with organizational health. It enables innovators to balance growth with impact, ensuring that scaling efforts do not compromise quality or values. For funders and practitioners, the framework provides a practical tool for strategy execution and continuous improvement, anchoring innovation in both accountability and adaptability.